May is National Egg Month! Even though eggs (or should we say, egg yolks) are nutrient powerhouses, they have gotten a bad rap—mostly due to their dietary cholesterol content and its presumed link to heart disease. Here’s what you need to know…
Eggstra Special Nutrition
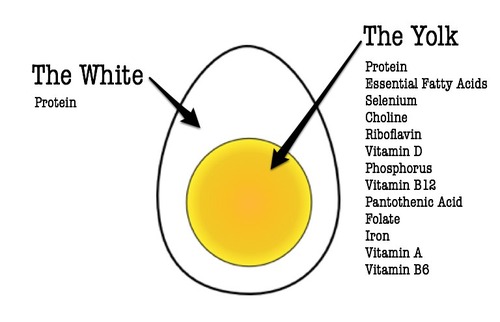
Eggs contain the most bioavailable protein of any food on earth—7 grams of protein per large egg, to be exact. They are loaded with 13 vitamins and minerals and all for a measly 70 calories!
Get Cracking
Research suggests that even though a whole egg has approximately 212 mg of cholesterol per large egg yolk, it has a marginal impact on our blood cholesterol, unless you have diabetes. Interestingly, it’s the types of fats in our diets (saturated vs. unsaturated) that influence our total cholesterol—lousy cholesterol (LDL) and healthy cholesterol (HDL)—more than the cholesterol found in foods.
In order to keep your cholesterol in check, you should reduce sources of saturated fat such as fatty pieces of meat, whole fat dairy (butter, cheese, whole milk), fried foods and baked foods. Consider swapping out the cheese for an egg and staying away from unhealthy pairings like bacon, cheese and buttered toast!
How Many Eggs is One Too Many?
Three yolks per week are recommended by the American Heart Association in order to limit excess amount of saturated fat and dietary cholesterol. If you do not have diabetes or are at risk for developing diabetes, most research has shown that one whole egg a day is generally safe for the heart.
How To Choose
You can use the guide below to understand egg labels and claims. Choose eggs that align with your needs and preferences! Note: The color of the egg shell specifies the breed of chicken and does not affect the quality, flavor or nutrition of the egg.
- Cage Free: Hens are not kept in cages and may or may not have outdoor access.
- Free Range: “Cage free” plus the birds must have continuous access to the outdoors.
- Vegetarian-Fed: Hens eat feed with no animal products or by-products (feather meal and hen meal are allowed in conventional chicken feed).
- Omega-3 Fortified: Hens are fed diets with flaxseed or algae, increasing the amounts of omega-3 fatty acids in the eggs by up to 20 times that of non-fortified eggs.
- Organic: “Free range” plus hens cannot be given antibiotics or growth hormones. Their feed is organic per the National Organic Standards.
- Pasture-Raised or Pastured: (Not legal terms) “Pastured eggs” come from hens that forage on bugs and grass (their natural diet). Often found at farmer’s markets.
Whats your favorite way to eat an egg? Share it with me on Bushwick Nutrition!
Co-Written by Debi Zvi RD, CDN and Alanna Cabrero MS, RD, CDN
Infographic by Debi Zvi, RD, CDN dzvi@nyhrc.com
Originally posted on NYHRC Tumblr
Reference: Skip the Egg Yolk, Skimp On Nutrition. Environmental Nutrition, March 2012.
Edited by Tamara Cabrero & NYHRC Team